
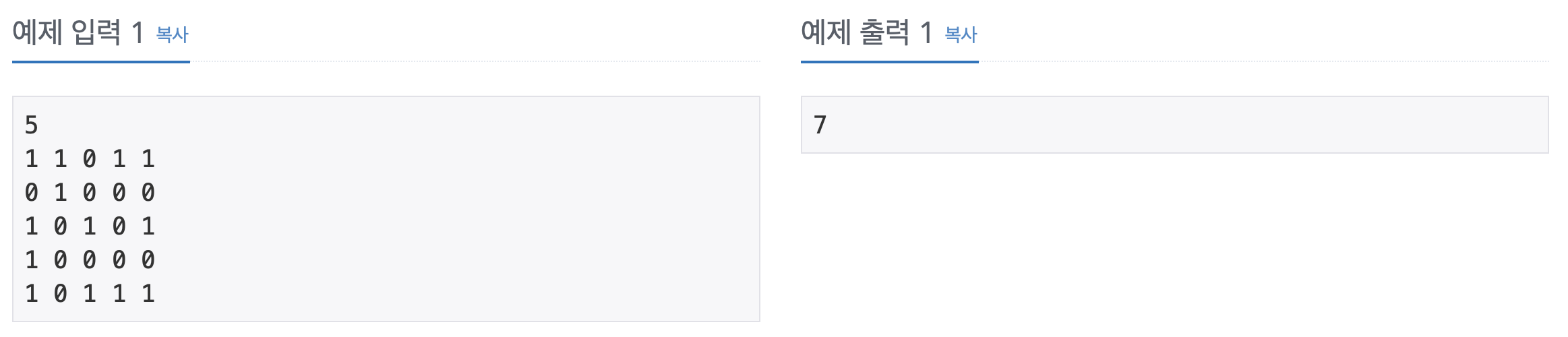
코드
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main {
static int n;
static int[][] map;
static ArrayList<Bishop> bishopWhite = new ArrayList<>();
static ArrayList<Bishop> bishopBlack = new ArrayList<>();
static public class Bishop {
int x, y;
public Bishop(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
static ArrayList<Bishop> bishops;
static int ans;
static int[][] dxdy = {{-1, -1}, {1, 1}, {-1, 1}, {1, -1}};
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
map = new int[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
map[i] = Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (map[i][j] == 1) {
if ((i + j) % 2 == 0) bishopBlack.add(new Bishop(j, i));
else bishopWhite.add(new Bishop(j, i));
}
}
}
int res = 0;
bishops = new ArrayList<>(bishopBlack);
findBishop(0, 0);
res += ans;
ans = 0;
bishops = new ArrayList<>(bishopWhite);
findBishop(0, 0);
res += ans;
bw.write(Integer.toString(res));
bw.flush();
}
private static void findBishop(int cnt, int res) {
if (cnt == bishops.size()) ans = Math.max(ans, res);
else {
Bishop bishop = bishops.get(cnt);
if (canPlaceBishop(bishop.y, bishop.x)) {
markMap(bishop.y, bishop.x, 3);
map[bishop.y][bishop.x] = 2;
findBishop(cnt + 1, res + 1);
map[bishop.y][bishop.x] = 1;
markMap(bishop.y, bishop.x, 1);
}
findBishop(cnt + 1, res);
}
}
private static void markMap(int y, int x, int idx) {
for (int[] ints : dxdy) {
int nextY = y + ints[0], nextX = x + ints[1];
while (nextX >= 0 && nextX < n && nextY >= 0 && nextY < n) {
if (map[nextY][nextX] == 2) return;
map[nextY][nextX] = idx;
nextY += ints[0];
nextX += ints[1];
}
}
}
private static boolean canPlaceBishop(int y, int x) {
if (map[y][x] == 3) return false;
for (int[] ints : dxdy) {
int nextY = y + ints[0], nextX = x + ints[1];
while (nextX >= 0 && nextX < n && nextY >= 0 && nextY < n) {
if (map[nextY][nextX] == 2) return false;
nextY += ints[0];
nextX += ints[1];
}
}
return true;
}
}코드 설명
처음 접근법은 백트래킹에서 인덱스 요소를 추가하는 것이었다.
그냥 백트래킹으로 돌려버리면 2^100이 되기 때문에 시간 초과가 발생하므로 하나의 비숍을 배치했을 때 그 비숍에 의해서 블락이 되어버리는 모든 칸을 3과 같은 특정 인덱스로 바꿔놓고 이후 백트래킹에서 칸의 값이 3이라면 더 이용하지 않고 끝낸다.
private static void findBishop(int cnt, int res) {
if (cnt == bishops.size()) ans = Math.max(ans, res);
else {
Bishop bishop = bishops.get(cnt);
if (canPlaceBishop(bishop.y, bishop.x)) {
markMap(bishop.y, bishop.x, 3);
map[bishop.y][bishop.x] = 2;
findBishop(cnt + 1, res + 1);
map[bishop.y][bishop.x] = 1;
markMap(bishop.y, bishop.x, 1);
}
findBishop(cnt + 1, res);
}
}
private static void markMap(int y, int x, int idx) {
for (int[] ints : dxdy) {
int nextY = y + ints[0], nextX = x + ints[1];
while (nextX >= 0 && nextX < n && nextY >= 0 && nextY < n) {
if (map[nextY][nextX] == 2) return;
map[nextY][nextX] = idx;
nextY += ints[0];
nextX += ints[1];
}
}
}
private static boolean canPlaceBishop(int y, int x) {
if (map[y][x] == 3) return false;
for (int[] ints : dxdy) {
int nextY = y + ints[0], nextX = x + ints[1];
while (nextX >= 0 && nextX < n && nextY >= 0 && nextY < n) {
if (map[nextY][nextX] == 2) return false;
nextY += ints[0];
nextX += ints[1];
}
}
return true;
}findBishop함수는 메인 백트래킹 함수이며 해당 비숍이 배치가 되는가 / 되지 않는가로 나누어 재귀를 진행한다.
canPlaceBishop함수는 해당 비숍을 배치할 수 있는지 확인한다.
먼저, 해당 칸 자체가 3으로 되어있을 경우 이전 비숍이 잡을 수 있는 사정거리 안이므로 배치하지 않고 끝낸다. 또한 해당 비숍의 사정거리 안에 다른 비숍이 이미 배치가 되어있다면 배치하지 않는다.
canPlaceBishop함수로 배치 여부를 확인했는데 배치를 할 수 있다면 markMap으로 비숍의 사정거리를 3으로 변경한다.
백트래킹 이후에는 markMap을 통해 다시 원래 상태로 복구시킨다.
이 과정을 처음에는 모호하게 코드를 작성했다.
boolean check = checkBishop(bishop.y, bishop.x, 3);
if (check) {
map[bishop.y][bishop.x] = 2;
findBishop(cnt + 1, res + 1);
map[bishop.y][bishop.x] = 1;
}
checkBishop(bishop.y, bishop.x, 1);이 checkBishop이 배치할 수 있는지 뿐만 아니라 맵을 변경하는 역할도 했는데 이럴 경우, 배치하지 않았을 때 맵을 돌리려는 시도가 있어 재귀를 깊숙하게 들어갔을 때 문제가 발생했다.
바꾼 코드는 조금 더 명확하게 역할을 나누고 배치를 할 수 있을 경우에만 맵을 돌리도록 했다.
이렇게 풀어도 시간초과를 피할 수 없었는데 찾아보니 두 비숍 분류로 나누는 것이 핵심이었다.
체스판은 검은색 타일과 하얀색 타일로 나뉘는데 비숍은 대각선에만 영향을 미쳐 다른 색 타일에 관여를 할 수 없기 때문에 흑, 백에 배치하는 비숍으로 나눠도 문제 풀이에 영향이 없다.
심지어 O(2 * 2^50)이므로 O(2^100) 보다 빠르다.
따라서 다음과 같이 나눠 저장해 백트래킹을 두 번 이용했다.
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
map[i] = Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (map[i][j] == 1) {
if ((i + j) % 2 == 0) bishopBlack.add(new Bishop(j, i));
else bishopWhite.add(new Bishop(j, i));
}
}
}
int res = 0;
bishops = new ArrayList<>(bishopBlack);
findBishop(0, 0);
res += ans;
ans = 0;
bishops = new ArrayList<>(bishopWhite);
findBishop(0, 0);
res += ans;인덱스로 나누어 접근하는 방법은 알기 쉬웠던 것 같은데 문제에서 제공하지 않은 정보인 체스판을 흑, 백으로 나누는 과정은 도출하기 너무 어려운 것 같다.
체스판을 흑 백으로 나누었을 경우 인덱스로 미리 체크를 하지 않아도 시간 초과가 발생하는지 여부는 확인하지 않았지만 위 코드가 더 효율적이긴 할 것 같다.
'코딩테스트 > 백준' 카테고리의 다른 글
| P.17143 낚시왕 (0) | 2023.10.02 |
|---|---|
| P.12850 본대 산책2 (0) | 2023.10.01 |
| P.1509 팰린드롬 분할 (0) | 2023.09.29 |
| P.16946 벽 부수고 이동하기 4 (0) | 2023.09.28 |
| P.10775 공항 (0) | 2023.09.27 |